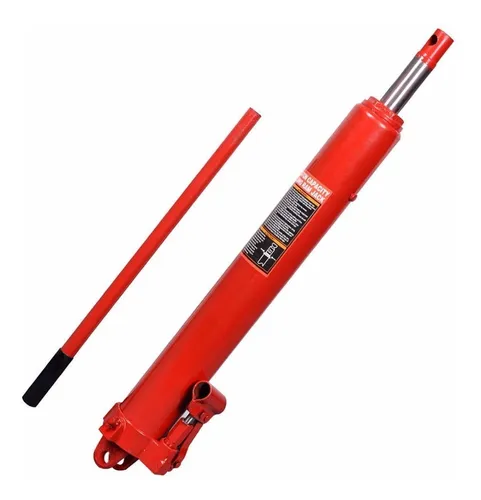
A hydraulic piston is a component of a hydraulic system that converts fluid pressure into mechanical force and motion. The piston is typically a cylindrical-shaped object that fits snugly within a cylinder or bore and moves back and forth in response to changes in fluid pressure.
The hydraulic piston typically consists of several key components, including:
- Piston head: The part of the piston that makes contact with the fluid and converts the fluid pressure into force.
- Piston rod: A slender rod that extends from the piston head and transmits the force generated by the piston to other components in the hydraulic system.
- Seals: Rubber or plastic rings or gaskets that are used to prevent fluid from leaking past the piston and into other parts of the hydraulic system.
Hydraulic pistons are used in a wide range of applications, from heavy machinery and construction equipment to automotive braking systems and industrial presses. They are often combined with other hydraulic components, such as pumps, valves, and actuators, to create a complete hydraulic system that can perform a variety of tasks.